Java Development Kit for Mac includes a wide variety of tools for streamlined developing, debugging, testing, and monitoring of Java applications. The package contains more than 30 individual tools and services which can be used to control every aspect of Java application development, from concept to final phase and deployment to end users. A free Java Development Environment designed for beginners, used by millions worldwide. Download and Install. Requires OS X 10.11 or later.
- Download Jdk 1.8 For Mac
- 1.8.0_10 Java Download For Mac Windows 7
- Java 1.6.0 11 Free Download
- Java 1.8.0 For Windows 10
- 1.8.0_10 Java Download For Mac Download
If you have to use a 32-bit Java VM on a 64-bit platform, download and use the 32-bit version of JCo. But the 64-bit variant should always be preferred on 64-bit platforms, if feasible. Some JVMs offer both modes: 32-bit as well as 64-bit. Download Java for OS X 2017-001 Java for macOS 2017-001 installs the legacy Java 6 runtime for macOS 10.13 High Sierra, macOS 10.12 Sierra, macOS 10.11 El Capitan, macOS 10.10 Yosemite, macOS 10.9 Mavericks, macOS 10.8 Mountain Lion, and macOS 10.7 Lion. Make sure you have a recent Java JRE installed on your system. Gephi is compatible with Java 7 and 8 versions. Download Free Java here. After the download completes, run the installer and follow the steps. After the download completes, click on the downloaded.dmg file. Drag the gephi application in your Application folder.
Geneious Prime 2020
| 2020_Full_Release 5 November 2019 2020 release notes | Longread sequence mapping with Minimap2 (external plugin) Fast and easy alignment of Oxford Nanopore and PacBio data to a reference sequence using an industry recommended tool, without the hassle of the command line |
| Clustal Omega replaces ClustalW for better, faster alignments Scale up your alignments with Clustal Omega, now included with Geneious Prime. The HMM alignment engine improves both quality and speed of alignments compared to the older ClustalW aligner. | |
| Better back translate and codon optimization New codon optimization algorithm lets you match the codon usage from your organism of choice by generating a new sequence, starting from either a protein or nucleotide sequence. Optionally eliminate rare codons and restriction sites. | |
| More accurate annotation of CDS features onto your plasmids Automatic annotation of plasmids is now smarter with adjustment of CDS boundaries to match the nearest valid ORF when annotating single-interval CDSs from your reference features database. | |
| Add your favorite tools to Geneious with improved Wrapper Plugin system Can’t wait for us to add your favorite command line aligner, tree builder or assembler? You might be able to add it yourself from right inside Geneious using the Wrapper Plugin Creator plugin. Coding skills are not required, though a good understanding of command line interfaces and file formats is. | |
| 2020.1 Update 10 March 2020 2020.1 release notes | Long Read de novo Assembly with Flye (external plugin) Fast de novo assembly of your raw Oxford Nanopore and PacBio long read sequences using Flye, suited to a wide range of applications including both single genome projects and metagenome assembly. |
| Import Metadata on to Sequences and other Documents Seamlessly attach new data from downstream analyses or other applications onto your sequences in Geneious, or update document fields, by importing columns from a CSV/TSV format spreadsheet onto documents that are already in Geneious. | |
| Annotate from Database Improvements Easily identify and annotate the best matched features from a database on your plasmids and other sequences using the new extended database of standard plasmid features provided with Geneious, or use your own sequences as reference. | |
| Codon Optimization and Back Translation Improvements Customize the codon optimization parameters for your model organism by defining short sequence motifs to exclude from your optimized sequence, while easily generating multiple co-optimized versions of your sequence simultaneously. | |
| Primer Specificity Testing Be confident your primers will only bind in a single location with automatic identification of any additional, off target, binding sites found when using Test with Saved Primers. Off-target information for the tested document will be added to the new primer annotations. | |
| Wrapper Plugin System Improvements Customize Geneious with your own plugins using the wrapper plugin system, which now supports de novo assemblers, and running supported linux-only tools via the Windows Linux Subsystem. | |
| 2020.2 Update 14 July 2020 2020.2 release notes | Analyze CRISPR Editing Results Easily align, cluster and visualize NGS reads from your CRISPR editing experiments. Analyze the frequency of variants and their protein effects from your application of choice, including HDR, NHEJ and base editors. |
| Enhanced Search Options Quickly access your documents, folders, analysis tools and recently viewed items from a single unified interface. | |
| Codon Optimization Improvements Hover over your optimized codons for more information on synonymous codons and their frequencies. |
Geneious Prime 2019
| 2019_Full_Release 6 November 2018 2019 release notes | Custom Codon Usage Tables Back translate and optimize codons using your own codon usage tables. Import standard formats from public databases or external codon analysis tools. |
| Rapid Manual Primer Design Select desired binding site in the Sequence View to see real-time display of length and melting point (Tm) then easily add a primer annotation with a convenient new button. | |
| Powerful Primer Annotation Display 5′ extensions (tails) on annotated primers are now displayed inside the sequence view to indicate the length of the extension, the nucleotides it contains and what functional elements are present such as restriction sites, spacers and tags. | |
| Simplified Testing and Annotation of Existing Primers Easily search all folders for primers that match a sequence of interest with the redesigned “Test with Saved Primers” operation. Copy and paste primers from other programs into the new “Add Primers” operation to find them on your target sequence in one step. | |
| Drag and Drop Sequence Export Export annotated sequences in GenBank format by simply dragging documents out of Geneious Prime and onto the desktop or into another program. | |
| Easy Extraction of PCR and Restriction Digest Products Shift click between two compatible primers or restriction enzymes for quick and easy extraction of their product from your sequence. | |
| Improved Protein Statistics Calculate on the fly statistics for protein sequences directly on nucleotide sequences within the Statistics panel, with new protein statistics added including charge at pH 7 and amino acid group counts. | |
| Improved GenBank Export Export the information you need with your sequences using the simplified, flexible options to include your own Meta-Data fields and allow or constrain export parameters to suit downstream applications. | |
| Publish Plugins via Internal Network Create a curated list of plugins to offer privately to members of your organization via your internal network. | |
| Usability Tweaks to Increase Efficiency Enjoy an improved table of primers, drag and drop backbone selection for cloning, easier workflow management, better defaults, a less cluttered Sequence View and many other little tweaks and improvements. | |
| 2019.1 Update 5 March 2019 2019.1 release notes | Customizable Text View – Sequence Layout Format to alter wrapping, numbering, sequence color and presence of reverse complement and translation |
| Customizable Text View – Alignment Layout Format to alter numbering, sequence color and highlighting of agreements/disagreements to consensus | |
| Customizable Text View – GenBank Format GenBank format available for all individual sequences | |
| Primer Specificity Primer specificity automatically tested within the template sequence when designing primers, and presence of any additional binding sites recorded on the primer annotation | |
| Primer Design Improvements Option to control the minimum distance between primers designed on the same strand – defaults to minimizing creation of duplicate primers when multiple primer pairs are designed together | |
| Annealed Oligo Cloning Added workflow to create a sequence with annotated overhangs representing the sticky ends created by annealing two partially overlapping oligos | |
| Restriction Enzymes Methylation sensitivity information shown in tool tip when mousing over a restriction enzyme | |
| 2019.2 Update 18 June 2019 2019.2 release notes | Sanger Sequencing Primer Design Quickly design primers for Sanger sequencing of vectors, inserts or other sequences |
| Vector NTI Database Import Easily import your complete Vector NTI database with simple drag and drop, for both Vector NTI Express and Advance databases. | |
| Improved Text View Formatting of Sequences and Alignments Support formatting and export of sequences in accordance with U.S. Patent Office requirements as well as other improvements. | |
| Primer Characteristics Quick and easy primer pairing in the Sequence View to link two primers of your choice and calculate pair dimer Tm and product size. | |
| Easier Shared Database Rollout Immediately access shared data and get straight to doing your research with a Geneious Shared database connections now able to be pre-configured by your IT team or admin when rolling out a version of Geneious Prime. Includes improved support for Windows authentication. |
Download Jdk 1.8 For Mac
R11
| R11_Full_Release 3 October 2017 11.0 release notes | Volcano Plots for RNA-Seq Expression Analysis Visualize gene expression in an interactive volcano plot that can be used to highlight and jump to differentially expressed genes. |
| Pretty PCA Plots Create beautiful PCA plots with better labelling and new visualization options. | |
| Silent Mutation Analysis for Restriction Sites Automatically identify point mutations in a coding sequence that will introduce a restriction site without affecting the protein. | |
| CRISPR Cpf1 Option Added support for CRISPR-Cpf1 with a 5’ PAM site. Find sites in A and T rich sequences and with higher cleaving efficiency in vivo. | |
| Create Enzyme Sets What’s in the freezer? No longer pull information from other sources. Now you can easily create your own enzyme sets. | |
| Better FASTQ Import Paired reads can be associated with each other during import and Geneious will do it’s best to guess how they’re paired. Read technology can also be set. | |
| Updated Mauve Plugin for Bacterial Genome Alignment Now includes support for sequence lists and the MCM operation for reordering contigs, making it possible to align draft genomes and perform genome finishing. | |
| R11.1 Update 6 March 2018 R11.1 release notes | SnapGene File Import Drop SnapGene *.dna sequence files into Geneious to seamlessly import sequences along with their annotations and other metadata. |
| CRISPR-Cpf1 Specificity Scoring Confidently pick the best CRISPR-cpf1 guide RNA sites using a new specificity score which is calculated from an off-target analysis against your database of choice. | |
| Smart NGS Import Drop any assortment of SAM, BAM, GFF, BED, and VCF files into Geneious to import in one easy step, even if you have a mixture of different samples and reference sequences. | |
| Better BLAST Server Management Set up several BLAST server mirrors at once and choose the best one each time you do a search. No more switching mirrors each time. | |
| NCBI BLAST Cloud Support It’s never been easier to set up your own BLAST mirror thanks to NCBI BLAST Cloud. If you set up a mirror in this way, Geneious can now connect to it natively. | |
| Concatenate by Index Concatenate sequence lists and alignments by index, rather than by name, which is super useful for merging paired reads that don’t quite overlap. | |
| CSV/TSV Export of Sequence Lists Export all of the sequences in a sequence list along with their metadata to CSV or TSV so you can drop them in Excel or similar for further analysis. |
R10
| R10_Full_Release 4 October 2016 10.0 release notes | Smarter Restriction Cloning Completely redesigned to be much simpler and more powerful. Includes automatic identification of compatible cut sites, and digestion and ligation with drag and drop ordering of fragments. |
| Alignment Masking Mask unreliable alignment sites for better tree building, without deleting data. Manage alignment masking patterns using annotation tracks and automatically mask sites according to user defined criteria. | |
| Improved Plasmid Viewer The new circular overview option helps you stay oriented by showing the bases of the sequence and the plasmid map alongside each other with synchronized editing, selection and scrolling. | |
| Chimera Filtering Filter chimeric reads by comparing to a reference database, which can be any sequence list or alignment. Choose between the bundled public domain UCHIME algorithm or the faster USEARCH implementation. | |
| Lineage View for Parent/Descendants Lineage View is now easier to access as a separate tab and details about your cloning operations are shown right next to the relationships. | |
| Assembly and Mapping Better structural variant mapping, a new workflow to build SNP trees by applying variants to a reference and better de novo assembly of Ion Torrent, 454, and PacBio CCS data. | |
| R10.1 Update 7 February 2017 R10.1 release notes | Improved Cloning Gibson and Golden Gate now has sequence view of fragments within the options. Gibson assembly can now saves primers for easy ordering |
| Annotate from Database Annotate nucleotide sequences from a protein database by comparing translations of the nucleotide sequence in all six frames with the protein database sequences | |
| Zip Import Zip files containing multiple files and sub-folders can now be imported | |
| Sequence Viewer Added ‘Copy Translation’ to translate selected regions of a nucleotide sequence (in right-click menu) | |
| SPAdes de novo assembler For MacOS/Linux: 64 bit OS is required. For Windows, 64 bit Windows 10 (with recent updates installed) is required. You also need to install additional Windows features (Instructions) | |
| Find CRISPR Sites Major performance improvements were made to the off-target scoring algorithm All CRISPR sites will now be scored against all potential off-target sites in every run Scoring CRISPR sites against off-targets now takes a seed region into account. This is a 10 bp region adjacent to the PAM site that can tolerate a maximum of 2 mismatches and 0 indels | |
| R10.2 Update 6 June 2017 R10.2 release notes | RNA-Seq Expression Analysis Compare Expression Levels now has the option to use DESeq2 for pairwise analysis with replicate samples and will produce a principle component analysis (PCA) plot for quality control. |
| Cloning Workflows Restriction Cloning, Gibson Assembly and Golden Gate can now be incorporated into Workflows. Automate your cloning procedures or perform high-throughput batch cloning. |
R9
| R9_Full_Release 7 October 2015 9.0 release notes | Golden Gate Intelligent handling of preconfigured Golden Gate parts and automatic designing of primers for new parts. |
| RNA- Seq and Structural Variant Mapping Map RNA-seq using existing annotated coding regions or discover novel intron and fusion genes during mapping. For DNA sequencing, you can now discover structural variants and annotate them, allowing for correct alignments of read-ends around deletions and structural rearrangements in heterozygous samples. | |
| Big Trees New search box for finding nodes and taxa, and automatic collapsing of sub-trees based on distances. Greatly improved performance when loading and rendering trees. | |
| Cutting edge CRISPR New scoring strategy for on-target activity. Options to control how many mismatches and indels are allowed when scoring against off-targets. | |
| VCF Export Easy exporting of single-sample variants. | |
| Tadpole Brand new and super-fast de novo assembler with a very low miss-assembly rate. | |
| Primer Design Improved the speed on larger sequences when a target region and product size range have been specified | |
Read filtering with built-in BBTools
| |
New Plugins
| |
| R9 Update 1 March 2016 R9.1 release notes | Even better support for HiDPI displays on Windows and Linux. Most importantly, the sequence and alignment view is now scaled according to your display. |
| Alignment and contig viewing redesigned “go to next” controls give more power in a more intuitive interface. | |
| Sequence view Updated to new modern font for high quality publications, cleaner plasmid maps and retina screens. | |
| Gibson Cloning now fully supports the full array of scarless methods including SLIC, SLiCE, CPEC, InFusion and GeneArt Seamless. | |
| Assembly New workflow to run batch reference mapping of many data sets against many references, matching them up by name. | |
| Trees Sequences in the multiple alignment are now highlighted according to coloring in the tree. | |
| Lineage Parents and descendants are now shown with more information about the steps that have been performed and an HTML report can be exported with the full lineage. |
R8
| R8_Full_Release 9 September 2014 8.0 release notes | 16S Biodiversity Tool A cloud-based tool that identifies high-throughput 16S rRNA amplicons from environmental samples using the RDP database, and visualizes biodiversity as interactive graphs and charts using a secure web viewer. |
| Sequence Classifier Plugin Taxonomically classifies an organic sample by how similar its DNA is to your own database of known sequences using a BLAST-like algorithm with multiple loci and trees to assist with identification. | |
| CRISPR Design Locate potential CRISPR target sites using innovative heatmap-style annotations to assess sites based on off-target interaction. | |
| Powerful NGS Assembly Longer contigs, scaffolding and greater accuracy. | |
| RNA-Seq Expression Analysis Brand new functionality for transcriptomics! | |
| Greater Workflow Configurability New Genome finishing workflow and more options for creating custom workflows | |
| Easier Plugin Development Add your favourite algorithm, database or visualization to Geneious or write a plugin for your own new program and share it with the community | |
| New Plugins Extended functionality for tree building and viewing, alignment and assembly. CRT – (by Chris Duran) Identifies existing known CRISPR sites in bacteria and archaea. FLASH – (by Dave O’Connor)- Merge paired sequencing reads using FLASH SeqPartitioner – (by Jed Barlow) – Partition allele multisets from multiple alignments Augustus – (by Michael Thon) Predict genes using the Augustus algorithm. EMBOSS Nucleotide Analysis – (previously bundled) Search for transcription factors, and predict protein coding regions. EMBOSS Protein Analysis – (previously bundled) Predict secondary structure, antigenic regions and signal cleavage sites. Go To Documents – Jump to documents by entering their unique IDs Find Big Folders Workflow – List the size of all folders in your local database Groovy Console – Opens a terminal window inside Geneious for scripting in the Groovy language. | |
| R8 Update 3 March, 2015 8.1 release notes | Choicer chooser Store commonly used sequences such as reference genomes, vectors and biological parts in separate folders from your working data, then easily choose them when you run Map to Reference or Gibson Assembly. |
| Sort by GC Content All newly created nucleotide alignments, contigs, sequence lists, and sequences have a %GC field in the document table. Sequences in alignments, contigs and lists can be sorted by %GC. | |
| Improved Primer Design for qPCR Batch design primers for many regions within a single sequence in one step, great for qPCR design. Primer design and testing now have an option to match each sequence in an alignment (instead of just the consensus) | |
| Extract more annotation information Now you can select upstream, downstream and intergenic regions of matching annotations. | |
| Mapping Qualities now included Geneious mapper produces mapping qualities, SAM/BAM import/export handles mapping qualities, contig viewer displays mapping quality in status bar, added mapping quality color scheme | |
| Integration with LIMS and external web-based systems Geneious documents can now be opened by clicking a link in external web-based systems. | |
| Easier Exporting for Newick and FASTA formats Documents can now be exported in the compressed .fasta.gz and .fastq.gz formats. Export Tree documents: Export to newick format may now include bootstrap support values | |
| New Plugins Blast2GO – All in one functional annotation tool and annotation data analysis. FreeBayes – Haplotype-based variant detector for single sample analysis. |
R7
| R7_Full_Release 3 September 2013 7.0 release notes | Workflows Easily create and share workflows based on your data and analysis. Try some of the built-in workflows or design your own. |
| Gibson Assembly One-step cloning of fragments using Gibson assembly including automated primer design and batch cloning/shuffling | |
| Codon Optimization Find rare codons or produce a fully optimized sequence based on a target organism and remove unwanted restriction sites at the same time. | |
| TOPO Cloning One-step cloning of fragments into a vector using TOPO | |
| Copy and Paste Annotations Annotations are now maintained when copying sequences! Highlight part of a sequence, copy with ctrl+c and then paste it using ctrl+v into another location and the annotations will be preserved. | |
| Better Coverage Analysis Get more meaning from your alignments with added visualization of coverage. | |
| New Plugins Extended functionality for tree building and viewing, alignment and assembly. RAxML – Randomized Axelerated Maximum Likelihood GARLI – Genetic Algorithm for Rapid Likelihood Inference FastTree – Approximately-maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees from alignments of nucleotide or protein sequences LastZ – BLAST-like alignment tool for the pairwise alignment of chromosome-sized nucleotide sequences Bowtie2 – Short read aligner Velvet – De-novo assembler for very short reads | |
| R7 Update 4 February 2014 7.1 release notes | Circular Assembly Geneious can create circular contigs in its famous sequence viewer making it easier to assemble genomes such as bacterial genomes and plasmids. |
| Trio Analysis The improved ‘compare annotation’ interface gives better results and more powerful options for SNP analysis and all results include annotation properties. | |
| Strip Alignment columns Build better trees! Remove columns with at least one ambiguity or strip two columns per codon. | |
| Extract more annotation information Now you can select upstream, downstream and intergenic regions of matching annotations. | |
| New Plugins TopHat – Fast splice junction mapper for RNA-Seq reads. MIRA – Specialized assembler for sequences with a high number of repeats |
R6
| R6_Full_Release 4 October 2012 6.0 release notes | Latest Primer3 engine Including brand new thermodynamic calculations that give you better stats on primers. |
| Automatic plasmid annotation No more manual searching. New automatic plasmid annotation lets you sort through your data faster than ever before, saving your time and your eyesight. | |
| Read Mapping New fine-tuning algorithm quickly generates accurate results using less memory. | |
| Enhanced Variant and SNP calling Eliminate false variants, annotate average quality, find variations within specified annotations. dbDNP and db_xref annotations now hyperlinked. | |
| Greater file format capability More options for VCF, SWF, FASTQ, SAM/BAM and zipped files | |
| New ‘info’ tab View lineage, history and edit common fields in properties such as description and organism | |
| R6 Update 7 February 2013 6.1 release notes | No more binding to known repeats The Primer Design tools now include a repeat library mispriming function that prevents binding to known repeats, saving you time. |
| BLAST+ Custom BLAST now supports BLAST+ for increased search performance. | |
| Enhanced DNA/RNA fold view The DNA/RNA fold view is now available on two sequences, showing how the two molecules bind to each other (using Vienna rnacofold 2.0.7). We’ve also updated the stats panel, improved the probability color scheme, and implemented new energy models, giving you greater visibility than ever. |
Downloads
Geneious Prime 2020.2
Geneious Prime 2020.1
Geneious Prime 2020
Geneious Prime 2019.2
Geneious Prime 2019.1
Geneious Prime 2019
Geneious R11.1
Geneious R11
Geneious R10.2
Geneious R10.1
Geneious R10
Geneious R9.1
Geneious R9
Geneious R8.1
Geneious R8
Geneious R7.1
Geneious R7
Geneious R6.1
Geneious R6
Geneious 5.6
Geneious 5.5
Geneious 5.4
Geneious 5.3
Geneious 5.1
Geneious 5.0
Geneious 4.8
Geneious 4.7
Geneious 4.6
Geneious 4.5
Geneious 4.0
Geneious 3.8
Geneious 3.7
Geneious 3.6
Geneious 3.5
Geneious 3.0
Geneious 2.5
Geneious 2.0
This page tells you how to download and install Java 8 and Eclipse on Mac OS X, and how to configure Eclipse.

1.8.0_10 Java Download For Mac Windows 7
Installing Java 8
Java 1.6.0 11 Free Download
Go to the Oracle website. You'll see something like this:
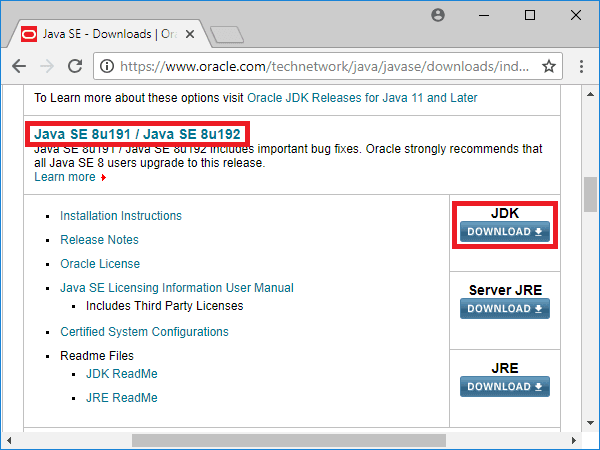
Scroll down until you see a heading beginning 'Java SE 8u65/8u66.' On the right, you'll see a Download button under the JDK header. Click it. The next screen will look like this:
Click the radio button next to 'Accept License Agreement' and then click on jdk-8u65-macosx-x64.dmg. You'll be asked whether to save the file that is going to be downloaded; click on Save File.
Open your Downloads folder, and double-click on jdk-8u65-macosx-x64.dmg. You'll see this window:
Double-click on the package icon, and follow the instructions to install. When the installation has completed, click on Done. At this point, you may close up the window and drag jdk-8u65-macosx-x64.dmg to the Trash.
Java 1.8.0 For Windows 10
Installing Eclipse
If you already have Eclipse installed on your Mac, you need to get rid of it. To do so, first quit Eclipse if you're currently running it. Then, go to your workspace folder (probably in Documents/workspace) and save anything there that you want to keep, because you're about to get rid of this folder. Next, drag the workspace folder to the Trash.
Go to your Applications folder. One way to get there is, from the Finder, type command-shift-A. You'll a folder named eclipse in there; drag the eclipse folder to the Trash. If you have an Eclipse icon in your dock, remove it from the dock.
Now you're ready to download and install the newest version of Eclipse. Go to this website. You'll see a window like this:
Mac file converter free download. Scroll down until you see 'Eclipse IDE for Java Developers' and click where it says 64 bit under Mac OS X.
You will see this window:
Click on the yellow download button. If asked, click on 'Open with Archive Utility (default)' and then click OK. The download might take a few minutes. You should not feel compelled to donate.
After the download completes, folders should automatically expand. If they don't, double-click on the .tar file. When that's done, you should see a folder named eclipse in your Downloads folder. When you open your Downloads folder, if you see Applications under the Favorites on the left side of the window, you should drag the eclipse folder into Applications. If you don't see Applications, then open a new window for Applications (from the Finder, command-shift-A), and drag the eclipse folder into Applications.
Open your Applications folder, and then open the eclipse folder. You'll see an item named Eclipse; if you like, drag its icon into the dock so that you'll be able to launch Eclipse easily.
Launch Eclipse. If you're asked whether you want to open it, of course you do; click Open. You'll see a window like this:
It will have your user name rather than mine (scot). Select where you want your workspace to be; I recommend the default of your Documents folder. Click the checkbox for using this location as the default, and then click OK.
You'll see a window like this:
Click on the Workbench arrow in the upper right that I've circled. You shouldn't see this screen again, even if you quit Eclipse and relaunch it.
You'll get an empty workbench like this:
We won't be using the 'Task List' and 'Connect Mylyn' windows. Click the 'x' on each to close it. Press the mouse on the Window menu item, then choose 'Perspective', and finally choose 'Save Perspective as..'. Enter 'cs10' for the name of this perspective and press return. Your workbench will now look like this:
You have now installed Eclipse!
Configuring Eclipse
You don't have to configure Eclipse the way I do, but you'll probably avoid some confusion if you do. Here's how.
1.8.0_10 Java Download For Mac Download
In the Eclipse menu bar, click on the Eclipse menu and then on 'Preferences..'. You'll see a window with two panes. On the left pane is a list of types of things you can configure.
Click on the triangle to the left of General. Then click on the triangle to the left of Appearance. Then click on 'Colors and Fonts.' You should see a window like this:
In the window in the middle, click on the triangle next to Java. Then double-click on 'Java Editor Text Font':
You'll see this window:
On the right, where you can select the size, click 12. Then close this window by clicking on the window's close button.
Close up the General preferences by clicking on the triangle to the left of General. Click the triangle next to Java and then click the triangle next to 'Code Style.' Then click Formatter. Here's what you should see:
Super hexagon free download mac. Click the button that says 'New..'. You'll see a window such as this one:
You can type in any profile name you like. I used 'CS 10':
Click OK.
You should see a window like this:
Change the tab size to 2:
You'll see that the indentation size automatically changes as well.
Click on 'Blank Lines,' and after 'Between import groups' and 'Before declarations of the same kind,' change the values 1 to 0:
Click on 'Control Statements,' and check the first four boxes as I've done here:
Click OK.
Now click on triangles to close up Java. Click on the triangle next to Run/Debug, and then click on Console:
Click on the green color sample next to 'Standard In text color.' You'll get a color picker:
Slide the slider on the right down, so that you get a dark green. (You're at Dartmouth. What other color could you possibly want?)
Close the color picker window by clicking its close button, and click OK again to close the Preferences window.
And you're done!
